자료형과 자료구조
데이터과학 자료형과 자료구조를 학습합니다.
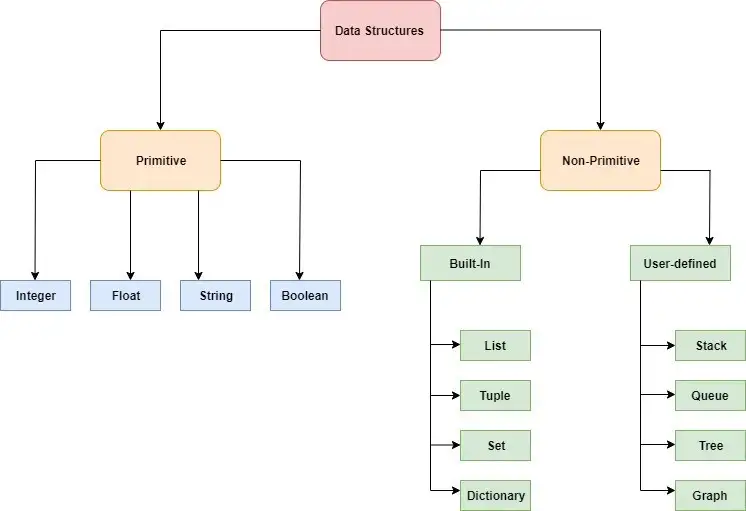
1 구분 방법
1.1 (Non) Primitive
자료형과 자료구조를 Primitive 를 기준으로 나눌 수도 있다.
- Primitive
- 정수형(Integer)
- 부동소수형(Float)
- 문자형(String)
- 부울형(Bloolean)
- Non-Primitive
- 내장 자료구조(Built-in)
- 리스트(List)
- 튜플(Tuple)
- 집합(Set)
- 사전(Dictionary)
- 사용자 정의(User-defined)
- 스택(Stack)
- 큐(Queue)
- 나무(Tree)
- 그래프(Graph)
- 내장 자료구조(Built-in)
1.2 일반적인 구분
- 변경가능 자료구조(Mutable data structures): 변경이 가능한 자료구조로 리스트(List), 사전(Dictionary), 집합(Sets)를 들 수 있다.
- 변경불가능 자료구조(Immutable data structures): 한번 생성되면 변경이 불가능한 자료구조로 튜플(Tuples), 문자열(Strings)을 들 수 있다.
- 순열 자료구조(Sequence data structures): 순열을 저정하는 자료구조로 리스트(list), 튜플(tuple), 문자열(string)을 들 수 있다.
1.3 데이터 저장 방식
- 선형 자료구조(Linear data structures): 데이터를 순차적으로 저장하는 자료구조로 배열(array), 연결 리스트(linked list), 큐(queue)를 들 수 있다.
- 비선형 자료구조(Non-linear data structures): 데이터가 순차적으로 저장되지 않는 자료구조로 나무(tree), 그래프(graph), 해쉬테이블(hash table)을 들 수 있다.
- 정적 자료구조(Static data structures): 정적 크기를 갖는 자료구조로 한번 생성되면 크기를 다시 재조정할 수 없는 자료구조로 배열(array)과 문자열(string)을 들 수 있다.
- 동적 자료구조(Dynamic data structures): 필요한 경우 크기를 자유자재로 조정할 수 있는 자료구조로 리스트(list), 사전(dictionary), 해쉬테이블(hash table)을 들 수 있다.
1.4 기타 구분 방식
- 순서있는 자료구조(Ordered data structures): 자료가 저장된 순서정보를 담고 있는 자료구조로 리스트(list), 튜플(tuple), 문자열(string)을 들 수 있다.
- 순서없는 자료구조(Unordered data structures): 자료가 저장된 순서정보를 담고 있지 않는 자료구조로 사전(dictionary)과 집합(set)을 들 수 있다.
- 연관 자료구조(Associative data structures): 키-값(key-value) 쌍을 갖는 자료구조로 키값을 사용해서 값(value)에 접근할 수 있다. 대표적으로 사전(dictionary)과 해쉬 테이블(hash table)을 들 수 있다.
- 스택 자료구조(Stack data structures): 스택을 구현한 자료구조
- 큐 자료구조(Queue data structures): 큐를 구현한 자료구조
- 나무 자료구조(Tree data structures): 나무모양을 갖는 자료구조