library(reticulate)
library(tidyverse)
reticulate::source_python("code/BERT/BERT_QnA.py")1 Context-Free and Context-based model
- Context-free models: Word2Vec, Glove, FastText
- Context-embedding models(transformer based models): BERT, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder
Context-free 모형은 단순하고 효율적이지만 텍스트의 뉴앙스를 비롯하여 의미를 잡아내는데 다소 미흡할 수 있다. 반면에 Context-based model은 강력하고 유연하지만 컴퓨팅 자원을 많이 사용하고 더 복잡하다.
2 질의응답
2.1 파이썬 코드
BERT 논문 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf의 초록(Abstract)에서 질의를 하고 관련 내용을 뽑아내는 코드를 다음과 같이 작성한다. (Ravichandiran, 2021)
# 질의응답 - 파이썬 코드
# 출처: https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Getting-Started-with-Google-BERT/tree/main/Chapter03
from transformers import BertForQuestionAnswering, BertTokenizer
import torch
model = BertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained('bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad')
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad')
# BERT 논문 Abstract: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf
question = "What does the 'B' in BERT stand for?"
abstract = "We introduce a new language representation model called BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Unlike recent language representation models (Peters et al., 2018a; Radford et al., 2018), BERT is designed to pretrain deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context in all layers. As a result, the pre-trained BERT model can be finetuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models for a wide range of tasks, such as question answering and language inference, without substantial task specific architecture modifications. BERT is conceptually simple and empirically powerful. It obtains new state-of-the-art results on eleven natural language processing tasks, including pushing the GLUE score to 80.5% (7.7% point absolute improvement), MultiNLI accuracy to 86.7% (4.6% absolute improvement), SQuAD v1.1 question answering Test F1 to 93.2 (1.5 point absolute improvement) and SQuAD v2.0 Test F1 to 83.1 (5.1 point absolute improvement)."
question = '[CLS] ' + question + '[SEP]'
abstract = abstract + '[SEP]'
question_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(question)
abstract_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(abstract)
tokens = question_tokens + abstract_tokens
input_ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
segment_ids = [0] * len(question_tokens) + [1] * len(abstract_tokens)
input_ids = torch.tensor([input_ids])
segment_ids = torch.tensor([segment_ids])
scores = model(input_ids, token_type_ids = segment_ids)
start_index = torch.argmax(scores['start_logits'])
end_index = torch.argmax(scores['end_logits'])
answer = ' '.join(tokens[start_index:end_index+1])
# print(' '.join(tokens[start_index:end_index+1]))
BERT 임베딩 모형을 사용해서 질문과 응답을 파이썬 코드로 작성하고 나서 그 결과값을 R에서 바록 읽어 후처리 하도록 한다.
2.2 질의응답 설정
BERT를 사용해서 질문과 응답을 준비한다.
py$question
#> [1] "[CLS] What does the 'B' in BERT stand for?[SEP]"py$abstract
#> [1] "We introduce a new language representation model called BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Unlike recent language representation models (Peters et al., 2018a; Radford et al., 2018), BERT is designed to pretrain deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context in all layers. As a result, the pre-trained BERT model can be finetuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models for a wide range of tasks, such as question answering and language inference, without substantial task specific architecture modifications. BERT is conceptually simple and empirically powerful. It obtains new state-of-the-art results on eleven natural language processing tasks, including pushing the GLUE score to 80.5% (7.7% point absolute improvement), MultiNLI accuracy to 86.7% (4.6% absolute improvement), SQuAD v1.1 question answering Test F1 to 93.2 (1.5 point absolute improvement) and SQuAD v2.0 Test F1 to 83.1 (5.1 point absolute improvement).[SEP]"2.3 질의응답 결과
# str_c(py$tokens[py$start_index$tolist()+1:py$end_index$tolist()+1], collapse = " ")
py$answer
#> [1] "bid ##ire ##ction ##al en ##code ##r representations from transformers"3 감성분석
3.1 파이썬 코드
IMDB 영화평점 텍스트에 담긴 감성분석을 BERT를 사용해서 수행한다.
# 감성분석 - 파이썬 코드
# 출처: https://wandb.ai/mukilan/BERT_Sentiment_Analysis/reports/An-Introduction-to-BERT-And-How-To-Use-It--VmlldzoyNTIyOTA1
import torch
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForSequenceClassification
df = pd.read_csv('https://gist.githubusercontent.com/Mukilan-Krishnakumar/e998ecf27d11b84fe6225db11c239bc6/raw/74dbac2b992235e555df9a0a4e4d7271680e7e45/imdb_movie_reviews.csv')
df = df.drop('sentiment',axis=1)
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment')
model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment')
def sentiment_movie_score(movie_review):
token = tokenizer.encode(movie_review, return_tensors = 'pt')
result = model(token)
return int(torch.argmax(result.logits))+1
df['sentiment'] = df['text'].apply(lambda x: sentiment_movie_score(x[:512]))3.2 감성분석 결과
senti_raw <- read_csv('https://gist.githubusercontent.com/Mukilan-Krishnakumar/e998ecf27d11b84fe6225db11c239bc6/raw/74dbac2b992235e555df9a0a4e4d7271680e7e45/imdb_movie_reviews.csv')
reticulate::source_python("code/BERT/BERT_sentiment.py")
senti_tbl <- senti_raw %>%
rename(label = sentiment) %>%
bind_cols(py$df %>% select(sentiment))
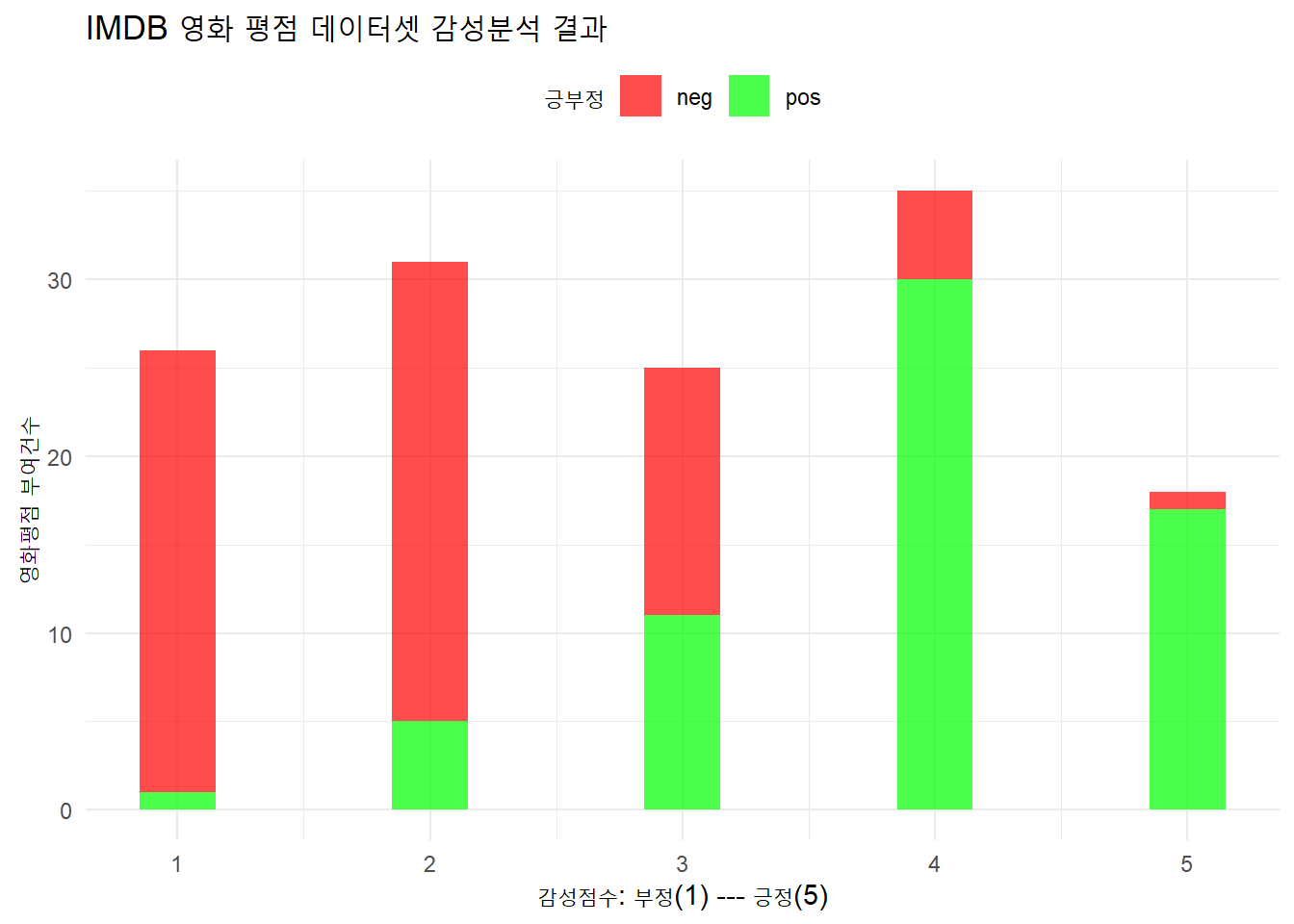
senti_tbl %>%
count(label, sentiment) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = sentiment, y = n, fill = label)) +
geom_col(width = 0.3, alpha = 0.7) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("red", "green")) +
labs(title = "IMDB 영화 평점 데이터셋 감성분석 결과",
x = "감성점수: 부정(1) --- 긍정(5)",
y = "영화평점 부여건수",
fill = "긍부정") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "top")3.3 후속 분석
평점 4점으로 예측된 영화 평점 중 긍부정 3개 리뷰를 뽑아 직접 살펴보자.
4 BERT 실용화
BERT가 좋은 성능을 보이는 것은 맞지만 너무 크기가 크기 때문에 실무적으로 사용하기에는 제약이 많다. 몇가지 기술이 개발되어 BERT를 사용하기 좋게 만드는 방법을 알아보자.
4.1 접근방법
- Quantization and Pruning
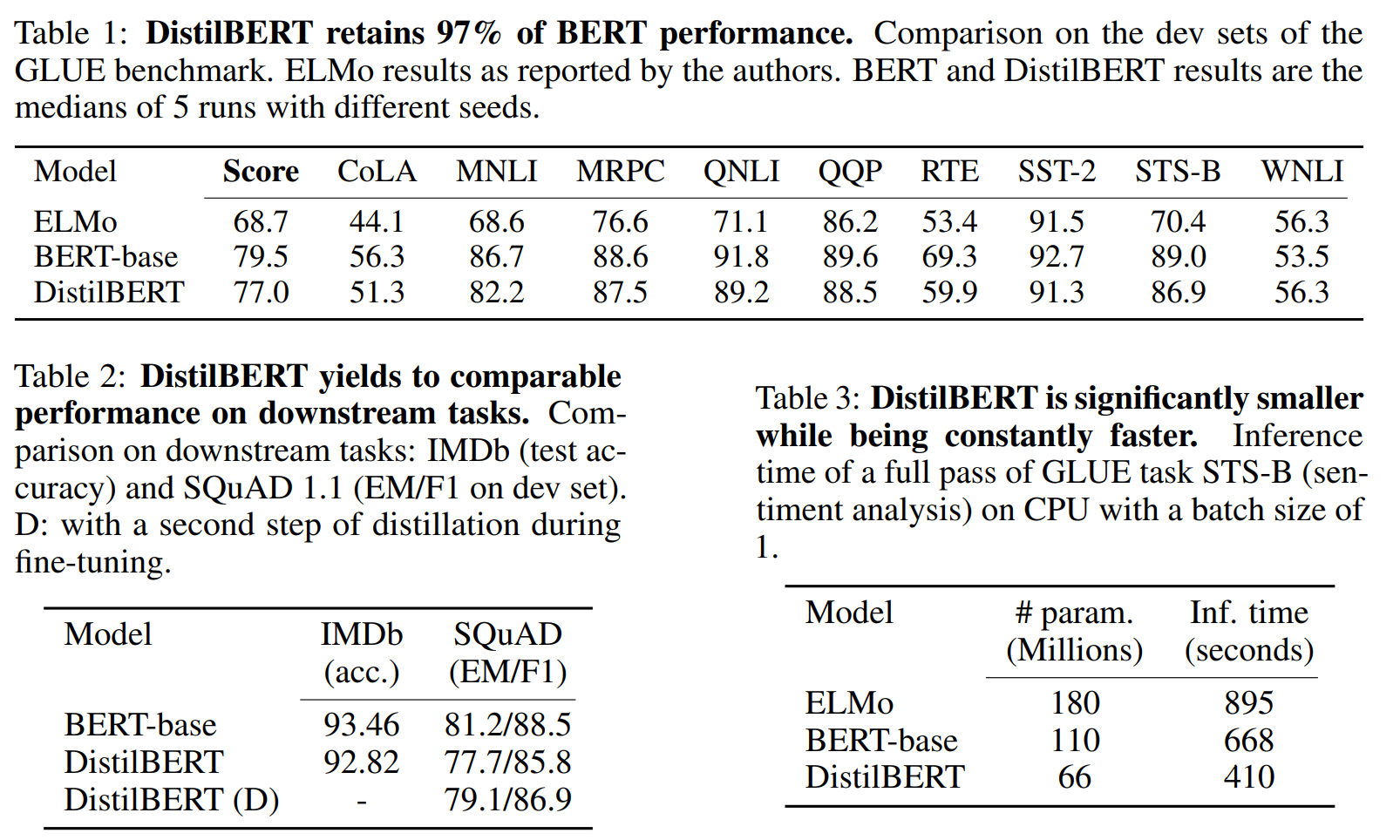
- DistilBERT: Knowledge Distillation
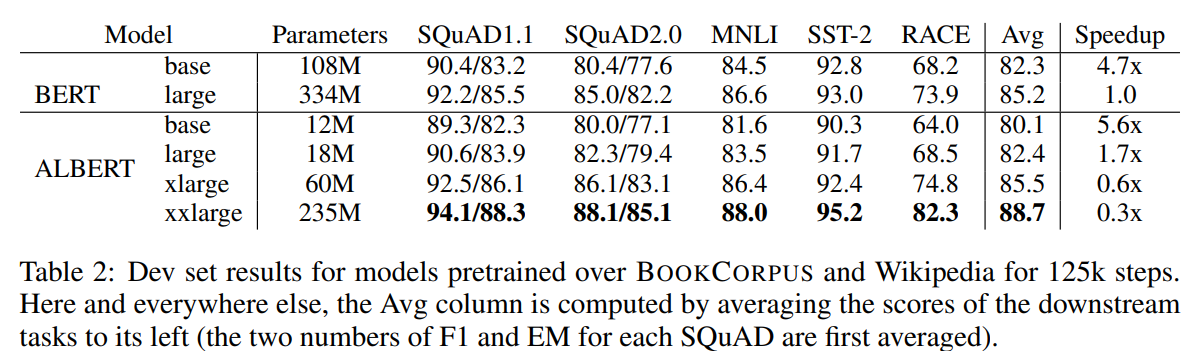
- ALBERT: A Lite BERT
4.2 성능비교
DistilBERT, A Lite BERT(ALBERT) 변형된 BERT 모형을 논문에 제시된 NLP 작업별 성능과 크기와 속도를 BERT-base 모형과 비교해보자.
참고문헌
Lan, Z., Chen, M., Goodman, S., Gimpel, K., Sharma, P., & Soricut, R. (2019). Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1909.11942.
Ravichandiran, S. (2021). Getting started with google BERT: Build and train state-of-the-art natural language processing models using BERT. Packt Publishing Ltd.
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., & Wolf, T. (2019). DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1910.01108.